Announcement: All pictures are from the book Jonathan Berk, Peter DeMarzo - Corporate Finance (2024).
MM理论讨论了 tax shield 之后,变成了
给出的 optimal capital structure 就是 interest 等于 earning before tax,这样就可以完全不交税、实现 investor 收益最大化。然而现实世界里面的公司不会这样做,甚至负债水平远低于 optimal leverage。这一章讨论的就是还有什么其他的因素影响了公司选择 capital structure。
在 perfect capital market 下,if a firm:
- has access to capital markets
- can issue new securities at a fair price
那么只要 assets exceeds liabilities 就不会 default。
Decline in value is not caused by bankruptcy. 项目成败决定是否会出现 economic distress;leverage 影响是否会有 financial distress.
Costs of Financial Distress
Bankcruptcy 会产生 direct 和 indirect costs。
Direct and Indirect
Direct costs: 公司破产过程需要聘请各种专家;creditor为了维护自己的利益,也需要聘请专家。弹性不大,导致公司规模越小,占比越高。
Workout 和 prepack 的区别在于,前者不会进入重组流程,而后者会。
Indirect costs:
- Customer:特别是需要保养维修等长期售后服务的,就会损失更多客户
- Supplier:收不回货款的风险
- Employee:特别是重人力资本的公司,留住key employee的成本很高
- Receivable:快倒闭了客户就会倾向于赖帐,reputation无所谓了
- fire sale:紧急出售资产导致折价
- inefficient liquidation:被迫出售资产影响后续运营
- chain effect:如果 creditor 很大一部分资金借给了这个公司,那 default 就会连锁 default
Indirect costs 会在 high leverage 的时候就产生影响,不一定要等到真的 bankcruptcy。
Calculation
确定 indirect costs 需要:
- 确定 losses to total firm value (including both creditor and equity holder)
- 确定 incremental losses associated with financial distress
例如 (risk free rate: 5%,破产costs 20 million):
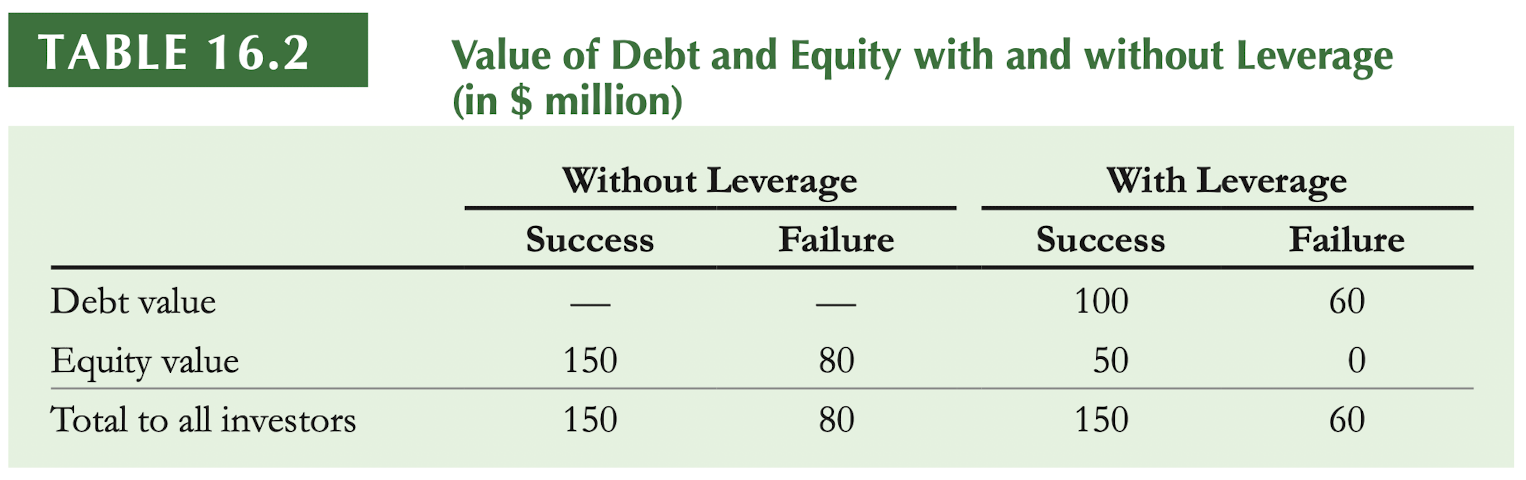
那么
所以 financial distress costs 导致了 9.52 million 的价值损失。
Creditor 不是傻子,所以一开始就不会支付那么高的价格给公司,所以:the original shareholders of a firm pay the PV of the costs associated with bankcruptcy and financial distress.
继续以上面的例子来计算,如果公司把面额 100m 的债券全部用来回购股票,那么:
- 原来的价值 $ V_U = 109.52 $,流通股数量 10m,股价就是 $ P = 109.52/10 = 10.952 $
- 新的资本结构下,公司价值是 $ V_L = 100 $,股价就是 $ P’ = 100 / 10 = 10 $
- 虽然债券面值是 100m,creditor 实际只会支付 76.19m(上面的 debt 的计算),所以回收的数量是 $ 76.19/10 = 7.619 $,剩下 2.381m 股
- 新的资本结构下 E 是 23.81m,除以新的流通股数 2.381m,股价就是 10
- 检查1和3的结果都是 10,检查成功
Factors
影响 financial distress 的 PV 的因素:
- probability
- liability 的 amount
- cash flow 和 asset value 的 volatility
- magnitude
- indirect costs 中的因素的 relative importance
- discount rate
- 这个的 $ \beta $ 跟 公司的 $\beta$ 符号相反;公司 $\beta$ 越大,这个 discount rate 越小,导致 PV(financial distress costs) 越大
Optimal
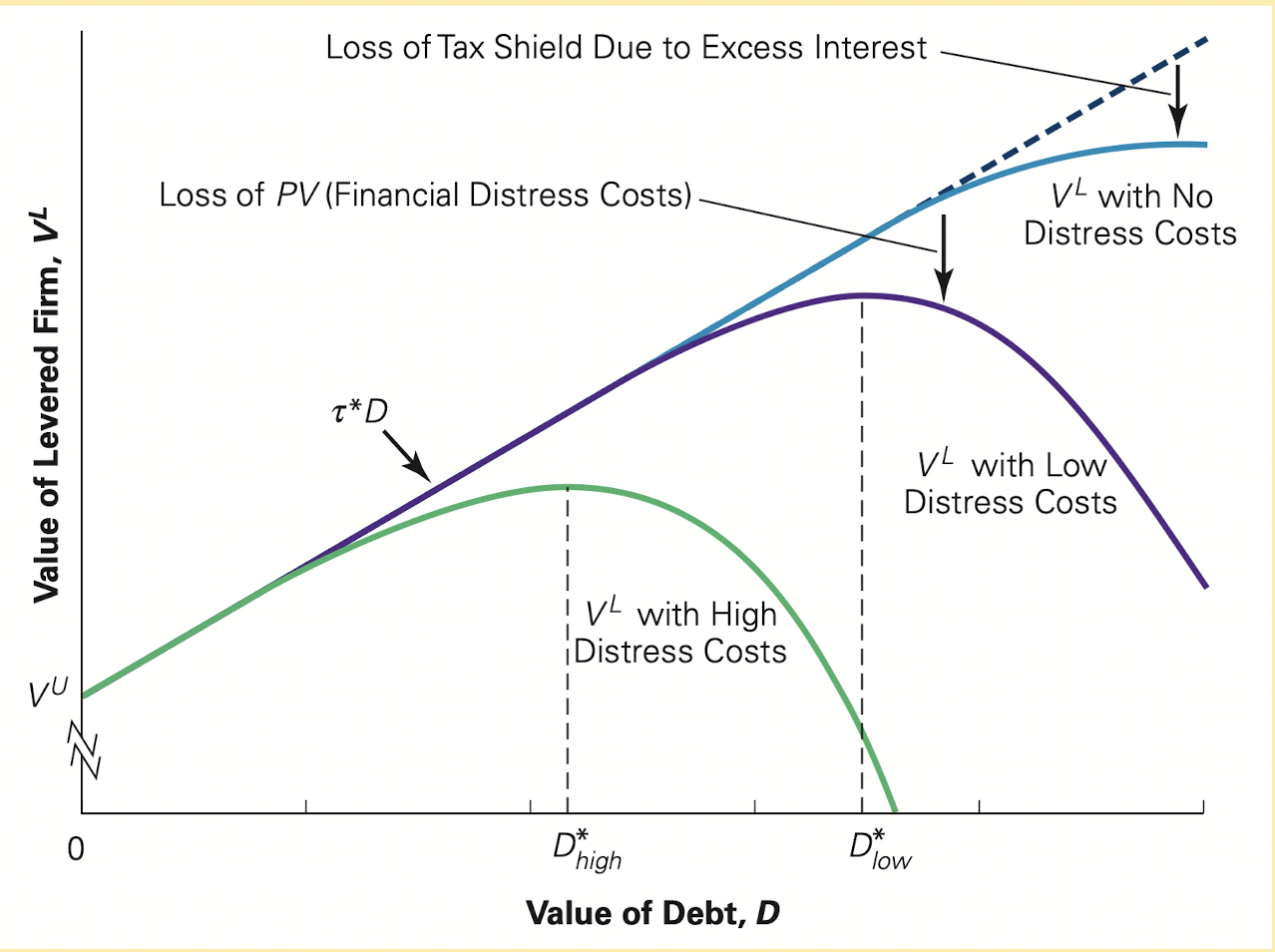
最优点是 $ max(PV(\text{Tax shield}) - PV(\text{Financial distress costs})) $ 的地方。
Agency Costs
- Overinvestment/asset substitution/excessive risk-taking
- higher for firms that can easily increase the risk of their investments
- Underinvestment/debt overhang
- high for firms that are likely to have profitable future growth opportunities requiring large investments.
- Cashing out
Overinvestment 能够解释为什么会投资 负NPV 的项目。比如什么都不做肯定会 default,但是搏一搏则有机会活下来;既然 have nothing to lose,就会投。

Creditor 不傻,所以一开始就不会支付那么高的价格给公司。
Underinvestment 能够解释为什么投资可以让公司不 default,但是公司不那么做。因为投资需要股东投入资金,但是最终的回报多数被 creditor 拿走了,对于股东来说是亏的。
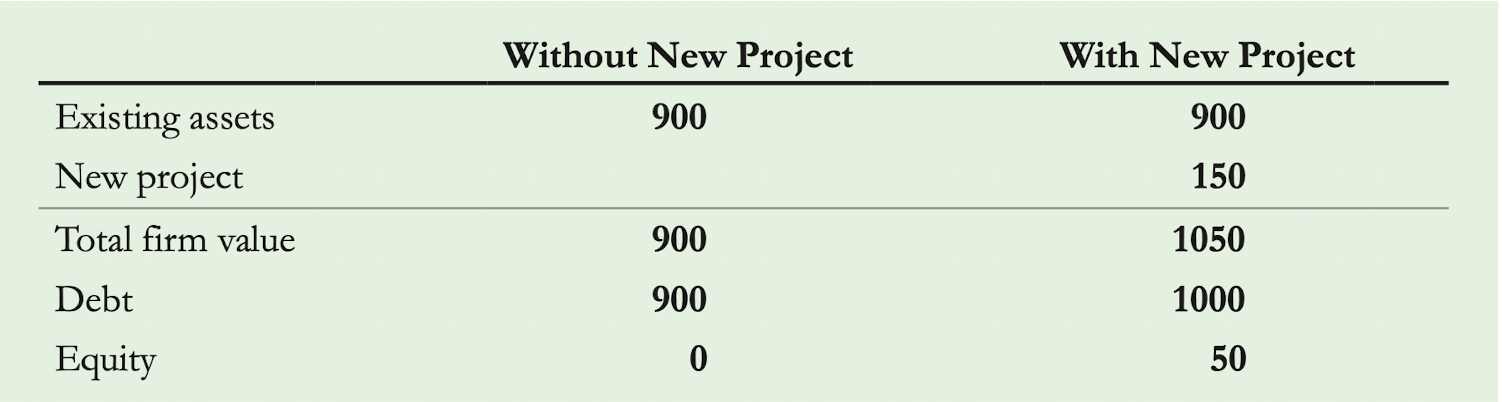 投入100,收回50;产出的150中100给了creditor。
投入100,收回50;产出的150中100给了creditor。
Cashing out: 公司一定会 default 的情况下,shareholders 在 default 前把有价值的资产低价卖掉、派发现金分红来把钱转走。
衡量 underinvestment 的方法,如果这个不等式成立,equity holder才会投资项目:
读作:profitability index exceeds the relative riskiness of the firm’s debt times its debt-equity ratio.
cashing out 的参数:
- 计算临界 NPV:$ {Investment} \times \frac{\beta_DD}{\beta_EE} $
- 临界 NPV + Investment = cash out 的资产价值上限
- 读作:公司可以 liquidate cash out 的资产价值上限 来派发 Investment 的现金分红来让股东受益
Factors
只有一个:debt amount
short-term debt 的 agency costs 最小,但是会增加 financial distress 的风险以及随之而来的成本。
Debt covenants 用来限制公司以损害债权人的利益来让股东获益,但是也会影响公司经营的灵活性导致丧失投资正NPV的机会,从而引入新的 costs。
Leverage Ratchet Effect
Once existing debt is in place:
- shareholders may have an incentive to increase leverage even if it decreases the value of the firm
- shareholders will not have an incentive to decrease leverage by buying back debt, even if it will increase the value of the firm.
Agency Benefits
Management entrenchment:manager以自己的利益优先来运作公司,甚至以投资者的利益为代价。
Manager over-invest的原因:
- Empire building: 投资能够扩大 size 而不是 profitability 的项目
- Overconfidence:对自己的公司通常都过于乐观
Concentration of ownership 能够减少 reduced effort 和 excessive spending on perks。
Free cash flow hypothesis:如果 FCF 过多,超过了投资所有能够带来正 NPV的项目所需要的数量,那么更容易发生 wasteful investment。
Leverage 带来的好处:
- 让公司必须考虑未来要支付的利息,减少 wasteful investment
- 由于存在 financial distress 而丢工作的风险,让 manager 能够认真经营公司、注重提高 profitability
- creditor 为了自身利益会监督 manager 的经营
Leverage 的其他用处
Credibility principle:Claims in one’s self-interest are credible only if they are supported by actions that would be too costly to take if the claims were untrue.
如果由于各种原因不可以公开信息,那就要选择其他方法来让投资者得到这个signal。
Lemons principle: When a seller has private information about the value of a good, buyers will discount the price they are willing to pay due to adverse selection.
- 宣布发行股票会导致价格降低(投资者认为这是overprice的信号)
- 宣布前股票价格 tends to rise
- 公司倾向于在信息不对称最小的时间窗口发行股票(比如earnings announcement之后)
为什么用debt:
- Signaling theory of debt:commit the firm to large future debt payments。如果default,manager就会丢工作,所以这种行动就会被理解为公司的未来很行。
- 避免股权融资引起的股价下降对原来的投资者不利(lemon principle)。
- 如果manager认为股票underpriced,就会倾向于用retained earnings或者debt来给项目融资(pecking order hypothesis)
- debt的价格基本被 interest rate 决定,而股价对 information 很敏感
除了考虑cost,管理层还会考虑股票是低估还是高估。所谓的 market timing view of capital structure.
Low leverage有两种可能:
- 没法使用 debt,被迫发行股票
- 现金太多了,用留存收益就能支持所有项目
- 预期未来会被 adverse selection,所以现在保持低杠杆来获得 financial flexibility
对于 capital structure 影响最大的是 tax。